Clinic Information
Sexually Transmitted Infections Information
Testing Recommendations and Options
Expedited Partner Services (EPT)
STI Prevention
Provider Information and Links
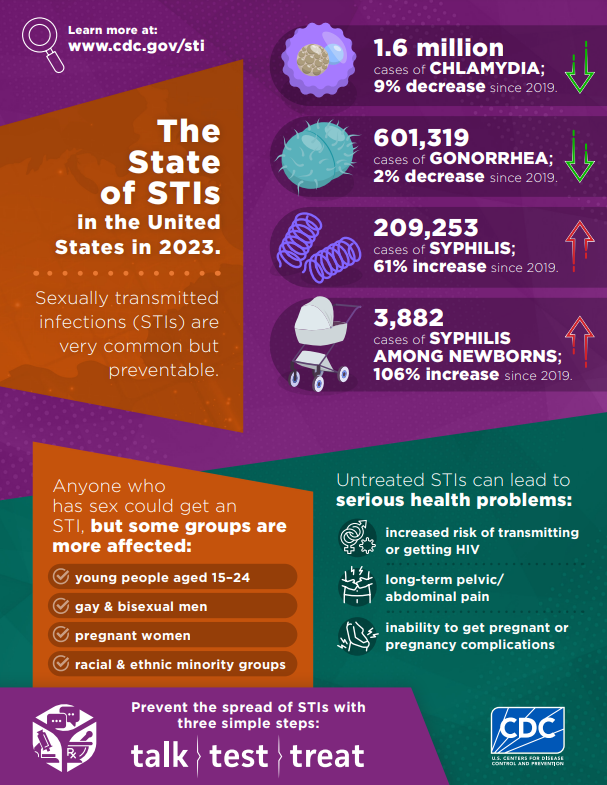
Sobering statistics from the CDC’s Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2023. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance, 2023 (cdc.gov)
Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) Information
|
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
|
Infections passed from person to person through sex, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Though uncommon, STIs can also be spread through other intimate physical contact. Many people with an STI have no signs or symptoms. You can feel healthy and not know that you have an STI. These infections are very common and millions occur every year in the United States. With proper protection, STIs are preventable. |
While there are more than 30 sexually transmitted infections, the most common are:
|
Chlamydia |
Chlamydia is a common STI that can cause infection among both men and women. Chlamydia often has no symptoms, but it can cause serious health problems, even without symptoms. If symptoms occur, they may not appear until several weeks after having sex with a partner who has chlamydia. For more information on Chlamydia: STD Facts - Chlamydia (cdc.gov) |
|
|
Gonorrhea |
Gonorrhea is an STI that can cause infection in the genitals, rectum, and throat. It is very common, especially among young people ages 15-24 years. Gonorrhea often has no symptoms, but it can cause serious health problems, even without symptoms. For more information on Gonorrhea: STD Facts - Gonorrhea (cdc.gov) |
|
|
Syphilis and Congenital Syphilis |
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can cause serious health problems without treatment. Infection develops in stages (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary). Each stage can have different signs and symptoms. You can get syphilis by direct contact with a syphilis sore during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Syphilis can spread from a mother with syphilis to her unborn baby, which results in Congenital Syphilis in the infant. For more information on Syphilis: STD Facts - Syphilis (cdc.gov) For more information on Congenital Syphilis: STD Facts - Congenital Syphilis (cdc.gov) |
|
|
HIV/AIDS |
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. If HIV is not treated, it can lead to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Sexual contact is one way that HIV can be transmitted. HIV can also be passed on to an infant during pregnancy, birth, and breastfeeding. AIDS is the third and most severe stage of HIV infection. It results in a badly damaged immune system that can cause an increasing number of infections and illnesses. For more information on HIV/AIDS visit: About HIV/AIDS | HIV Basics | HIV/AIDS | CDC |
|
|
Mpox |
Mpox is an infectious viral disease that anyone can get through close, personal, often skin- to-skin contact. The rash may look like pimples, blisters, or sores, often with an earlier flu-like illness. Vaccines are available. Mpox does not usually cause serious illness, however, it can result in hospitalization or death. While New Yorkers should not be alarmed, everyone should stay informed about Mpox. For an update on Mpox in New York State, including in St. Lawrence County, please visit: Mpox (ny.gov) For more information on Mpox visit: Mpox | Poxvirus | CDC |
|
|
HPV |
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is the most common STI in the United States. It is spread by having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has the virus. In most cases (9 out of 10), HPV goes away on its own within two years without health problems. But when HPV does not go away, it can cause health problems like genital warts and cancer. There are vaccines that can stop these health problems from happening. For more information on HPV visit: STD Facts - Human papillomavirus (HPV) (cdc.gov)
|
|
|
Other STI’s |
Find information on other STIs by visiting: CDC - STI Fact Sheets |
Testing/Screening Recommendations and Options
For anyone who is sexually active, getting tested for STIs regularly is one of the most important steps you can take to protect yourself and others. Have a conversation about your sexual history and STI testing with your doctor to find out if you should be tested for STIs.
If you are not comfortable talking with your regular health care provider about STIs, you can look for one of the free, confidential STI clinics in the area.
Testing recommendations:
|
Chlamydia and Gonorrhea
|
Everyone who is pregnant should be tested during each pregnancy! Anyone with symptoms or had a sex partner test positive! Every Year if you:
Every 3-6 Months if you:
|
|
Syphilis
There has been a significant rise in cases of Syphilis and Congenital Syphilis in New York State! |
During Pregnancy:
Screen as Needed if you:
Every Year if you:
Every 3-6 Months if you are:
|
|
HIV |
During Pregnancy:
At Least Once or as Needed:
Every Year if you are:
|
Free Confidential Testing locations in our area:
|
EPT (Expedited Partner Therapy)

For more information on EPT visit: Partner Services is HIV/STI Prevention (ny.gov)
STI Prevention:
|
Sexually transmitted infections ARE preventable! Here are the steps you can take to keep yourself and any sex partners safe |
|
|
Know the facts! |
Learn the information you need to know on how infections are spread, the symptoms you may experience, when to get tested and how the infection can be treated. Knowledge is a key to prevention. You can learn by accessing CDC - STI Fact Sheets |
|
Abstinence |
The only way to completely avoid STI’s is to not have any form of sex. |
|
Condoms |
When used correctly and consistently, condoms reduce the risk of infection for all STIs. You can still be infected by certain infections that are transmitted through skin-to-skin contact. Learn more condoms, including female condoms here. Condom Use | CDC |
|
Limit the number of sex partners |
|
|
Get vaccinated |
HPV, Mpox, and Hepatitis B all have vaccines available to help prevent infection. Talk to your health care provider or click here to see information on the immunization program at St. Lawrence County Public Health. |
|
Get tested |
So many STIs have no symptoms. Standard screening or screening you know you have had a partner test positive can help prevent the spread of infection. Click here to see testing recommendations and information. |
Links to helpful material and resources:
- Expedited Partner Therapy:Expedited Partner Therapy (cdc.gov)
- Legal Status of EPT in New York State:
From the NYS DOH
|
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) is the clinical practice of providing individuals with medication or a prescription to deliver to their sexual partner(s) as presumptive treatment for a sexually transmitted infection (STI), without completing a clinical assessment of those partners. On January 1, 2020 Chapter 298 of the Laws of 2019 went into effect, expanding New York State Public Health Law §2312 to permit expedited treatment for STIs for which the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the use of expedited therapy. Prior to this change, EPT was allowable in New York State for chlamydia only. The CDC currently includes EPT as an option for management of sex partner(s) for chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis), gonorrhea (N. Gonorrhoeae), and/or trichomoniasis (Trichomonas vaginalis) sexually transmitted bacterial infections. |
- 2021 STI Treatment Guidelines: STI Treatment Guidelines (cdc.gov)
- Congenital Syphilis Information for Providers
- STI Provider Advisories: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) (ny.gov)
- DOH Information for Providers Home Page Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) (ny.gov)

.png)
